The control exerted by the levels of ATP ADP and AMP within the cell is illustrated by the regulatory mechanisms of glycolysis and the TCA cycle. When ATP levels are low.

File End Product Inhibition Of Threonine To Isoleucine Png Wikimedia Commons
Describe the control of metabolic pathways by enzymes through end-product inhibition also called a negative feedback loop.

. End productinhibitor is final product of chainpathway. End-product inhibition or feedback inhibition is a form of negative feedback by which metabolic pathways can be controlled. Understandings metabolic pathways consist of chains and cycles of enzyme-catalysed reactions.
This inhibition is involved in the regulation of how much of the end products to be produced. The product binds to an allosteric site and temporarily inactivates the enzyme via non-competitive inhibition. Describe allosteric regulation of enzyme activity.
C25 Explain the control of metabolic pathways by end-product inhibition including the role of allosteric sites. Therefore less of the end product gets produced and by inhibiting the first enzyme it also prevents the formation of intermediates. Metabolic pathways consist of chains and cycles of enzyme-catalysed reactions.
The production of both amino acids and nucleotides is controlled through feedback inhibition. It is the correct shape to bind with the allosteric site of the first enzyme. Isoleucine is end product.
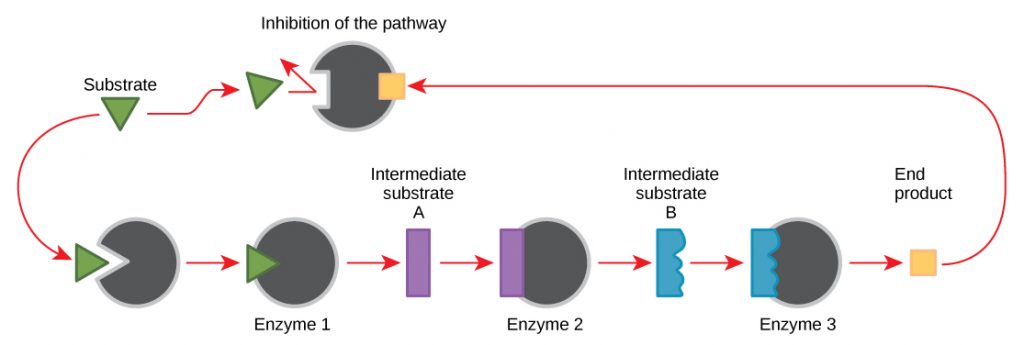
When the levels of the end product decrease the enzymes start to work again and the metabolic pathway is. These nucleotides also serve to govern the occurrence of the opposite pathway gluconeogenesis and to avoid mutual interference of the catabolic and anabolic sequences. In end-product inhibition the final product in a series of reactions inhibits an enzyme from an earlier step in the sequence.
April 13 2015 C24 Explain the difference between competitive and non-competitive inhibition with reference to one example of each. End-product inhibition is a cellular control mechanism in which the activity of enzymes is is inhibited by the enzymes end product. Illustrate end-product inhibition of the threonine to isoleucine metabolic pathway.
Feedback inhibition where the end product of the pathway inhibits an upstream process is an important regulatory mechanism in cells. The final product is called a feedbackproduct which is an allosteric inhibitor. Therefore less of the end product gets produced and by inhibiting the first enzyme it also prevents the formation of intermediates.
Benefit of end-production inhibition. Metabolism is chainsweb of enzyme-catalyzed reactions. Enzymes lower the activation energy of the chemical reactions that they catalyse.
Enzyme inhibitors can be competitive or non-competitive. All metabolic pathways have to be regulated and controlled to stop the build-up of an end product that isnt needed. Feedback inhibition refers to the inhibition of enzymes by the end product of the biochemical pathway due to binding with the regulatory site of the enzyme and preventing the binding of the substrate to the enzyme.
End-product inhibition is also termed feedback inhibition. Each reaction is enzyme-catalyzed and thus represents the point of control. Because of its negative feedback ans binding to the allosteric site it slows the rate of product formation.
Figure 11 Metabolic pathways are a series of reactions catalyzed by multiple enzymes. 81A1 End-product inhibition of the pathway that converts threonine is isoleucine. It thus distorts the shape of the.
Explain the control of metabolic pathways. When there is an excess of end-product the whole metabolic pathway is shut down as the end product inhibits the first enzyme of the pathway. Name an example of end-production inhibition.
Products of one reaction become substrates for the next. Some enzymes are allosteric. Metabolic pathways can be controlled by end-product inhibition.
A metabolic pathway is a series of reactions carried out in a particular sequence. The cell can control a metabolic pathway by the presence or absence of a. Another way a metabolic pathway can be controlled is by feedback inhibition.
Allosteric control end-product. Making it easier to regulate metabolic pathways. When the levels of the end product decrease the enzymes start to work again and the metabolic pathway is.
This is when the end product in a metabolic. End-product inhibition of the pathway that converts. Outline the control of metabolism by end-product inhibition 5 a.
-metabolic pathway regulated according to the requirement for its end-product. Outline the mechanism and benefit of end-product inhibition. OR metabolic pathway is a chain of enzyme-catalyzed reactions.
Enzyme inhibitors can be competitive or non-competitive. When there is an excess of end-product the whole metabolic pathway is shut down as the end product inhibits the first enzyme of the pathway. Produce a schematic of the process.
-negative feedback since increased level of product-decreases rate of its own production. Metabolic pathways can be controlled by end-product inhibition applications and skills application. In simple words the inhibition of an enzyme by its product is called feedback inhibition.
Explain the control of metabolic pathways by end-product inhibition including the role of allosteric sites allostery is a form of non-competitive inhibition which can be used to regulate metabolic. The regulation of ATP formation by phosphofructokinase an enzyme in glycolysis. 81U4 Metabolic pathways can be controlled by end-product inhibition.
-end-product of a pathway can inhibit enzyme needed for the first step in metabolic pathway. Inhibitsbinds toblocks the first enzyme in chainpathway. Enzymes lower the activation energy of the chemical reactions that they catalyse.

End Product Inhibition 8 1 3 Ib Biology Hl Youtube

Metabolism End Product Inhibition Britannica
Feedback Inhibition In Metabolic Pathways Principles Of Biology
0 Comments